Seasonal Planting Plans for Small Vegetable Gardens can transform your gardening experience into something deeply rewarding. Planning a small vegetable garden is an enriching journey, especially when you embrace the nuances of seasonal planting. Each season brings its own set of opportunities. Over the years, I’ve experimented with different techniques and strategies that have improved my yields and deepened my connection to this age-old practice. I’m excited to share this comprehensive guide to help you navigate the art and science of planting with the seasons, drawing from my journey and lessons..
Understanding Seasonal Planting
The Importance of Timing in Vegetable Gardening
Timing is everything in gardening. Planting at the right time ensures that your vegetables thrive in optimal conditions, leading to better yields and healthier plants. Each season brings unique opportunities and challenges, and learning to adapt to these can significantly improve your gardening results.
For instance, planting too early in spring might expose your crops to frost, stunting their growth or killing young seedlings.
Conversely, planting too late in summer could result in stunted growth due to heat stress or shortened maturity windows. I’ve experienced both scenarios, and the lessons have been invaluable in fine-tuning my planting schedule.
Understanding these nuances can make or break your gardening success, especially in a small garden where every plant matters and there’s little room for error. A well-timed planting schedule boosts productivity and makes the entire gardening process more enjoyable and less stressful. Design layouts that work with seasonal planting schedules.
How Climate Affects Your Planting Schedule
Your local climate is crucial in determining what and when to plant. Living in a region with distinct seasons, I’ve learned the importance of tailoring my planting schedule to match the weather patterns, as this ensures optimal growth and yield.
Tools like the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map or your local agricultural extension office can provide insights into your area’s growing conditions. For example, in warmer climates, gardeners can often enjoy the luxury of two full growing seasons—spring and fall—each offering unique planting opportunities.
Meanwhile, cooler regions may require focusing on shorter, more intensive growing periods, making every planting decision critical.
The impact of climate variability on planting schedules cannot be overstated, as I witnessed firsthand during a recent consultation at Moholo Farms, near Kgare Village in Botswana (Coordinates: -22.5226, 26.0297).
The client planted medium-maturity white maize in mid-October 2024 (Botswana’s climate is semi-arid to arid, characterized by hot, dry conditions with distinct wet and dry seasons). A severe heatwave caused significant heat stress on maize crops, visibly affecting their development. Shortly after, heavy rains arrived and persisted for two weeks, further complicating the situation.
The excess moisture, combined with the earlier stress, resulted in poor pollination, leading to irregularly shaped cobs and missing kernels—a clear indication of environmental stresses at play.
Adding to the challenge, the presence of Fall Army Worms exacerbated crop losses, as they thrived in damp conditions, damaging leaves, and further stunting growth. These experiences underline the importance of adapting planting schedules and pest management strategies to unpredictable climate patterns.
For small gardens, the lessons from larger-scale agriculture can be invaluable: choosing resilient crop varieties, monitoring weather forecasts, and being prepared to manage pests proactively are critical for success in any growing environment.

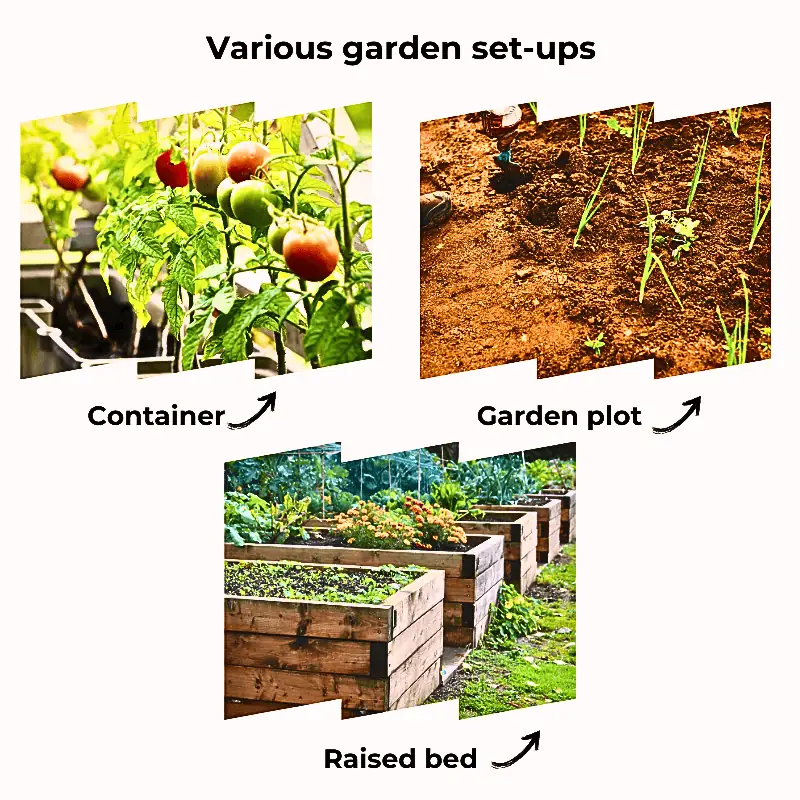
Assessing Your Space: Container vs. In-Ground Gardening
Not all of us have sprawling gardens to work with, and that’s okay. Small spaces can be just as productive with the proper planning. When I started, I experimented with container gardening and traditional in-ground plots.
While containers are great for flexibility and portability, in-ground gardens offer more room for root growth and soil diversity. Raised beds, another popular option, provide a middle ground, combining the benefits of both approaches while improving drainage and accessibility.
Selecting the Right Vegetables for Each Season
Choosing the right crops is essential. Over the years, I’ve discovered that leafy greens like lettuce and spinach thrive in cooler months, while tomatoes and peppers love the summer heat.
Root vegetables such as carrots and radishes are versatile and can adapt to multiple seasons. Seasonal rotation optimizes yields and helps maintain soil health by reducing the risk of pest and disease buildup.
Spring Planting Strategies
Cool-Season Crops: What to Plant Early
Spring is a magical time for gardeners. As the frost recedes, it’s the perfect season to plant cool-weather crops like peas, radishes, and kale. These hardy vegetables thrive in the cool, moist soil of early spring.
I often use row covers to protect young seedlings from unexpected cold snaps while extending the growing season.
Preparing Your Soil for Spring Growth
Healthy soil is the foundation of a successful garden. No matter which hemisphere you live in enriching your soil with compost and organic matter is always good start.
This practice boosts fertility and ensures the soil retains moisture better as the season progresses. Adding a balanced, slow-release fertilizer tailored to the needs of your chosen crops can give your plants a strong start.

Summer Gardening Tips
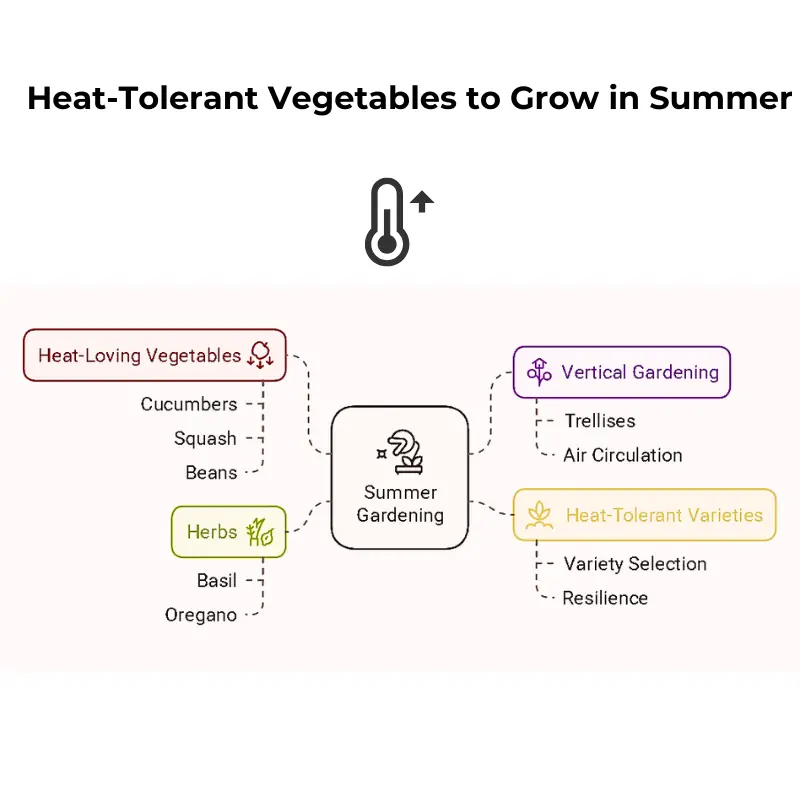
Heat-Tolerant Vegetables to Grow in Summer
Summer brings longer days and warmer temperatures, perfect for heat-loving vegetables like cucumbers, squash, and beans. To maximize space, I often use vertical trellises for climbing plants, improving air circulation and making harvesting easier.
Additionally, I’ve found that selecting varieties bred explicitly for heat tolerance ensures better resilience during the peak summer heat. Herbs like basil and oregano also flourish this season, adding flavor to your kitchen and a touch of vibrant greenery to your garden.
Managing Water and Nutrients During Hot Months
One summer lesson I learned the hard way is the importance of consistent watering. Early morning irrigation helps prevent evaporation, and mulching keeps the soil cool and moist.
Drip irrigation systems can be a lifesaver, especially during peak heat. Regular feeding with organic fertilizers ensures plants get the nutrients they need to thrive, and shading delicate crops can prevent sunscald.
Fall Planting Techniques
Best Vegetables for Late-Season Harvests
As summer winds down, fall offers a second chance to grow. Root vegetables like carrots and beets and brassicas like broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage are excellent choices for a fall harvest.
I’ve found that planting these crops in late summer allows for a bountiful yield before the first frost. Additionally, experimenting with staggered planting can help ensure a continuous harvest throughout the season.
Floating row covers can protect these crops from early frosts, extending their growing period and safeguarding against sudden temperature drops.
Preparing Your Garden for Winter: Cover Crops and Mulching
Winter preparation is key to maintaining soil health. Planting cover crops like clover, vetch, or rye adds organic matter, prevents soil erosion, and supports beneficial soil organisms during the dormant season.
Adding a thick layer of mulch protects the soil from temperature fluctuations, helps retain essential moisture, and suppresses weed growth.
Together, these steps create an environment that ensures your garden is primed for success when spring returns, giving your plants the best possible start. Check out more valuable tips for cooler climates on Storm.
Companion Planting for Small Gardens
Benefits of Companion Planting in Limited Spaces
Companion planting is a game-changer for small gardens. Pairing plants like tomatoes and basil saves space, boosts growth, and repels pests. Over the years, I’ve seen how strategic planting combinations can enhance overall garden productivity while reducing the need for chemical pest controls.
Top Companion Plants for Common Vegetables
My favorite combinations include marigolds with squash to deter pests and carrots with onions to save space and ward off insects. Beans and corn are another classic pairing, as the beans fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting the corn.
Experimenting with different pairings has added a fun and educational element to my gardening journey.
For more detailed information on companion planting and how it can benefit your small garden, check out our comprehensive guide here
Maintaining Your Garden Throughout the Seasons
Regular Maintenance: Weeding, Watering, and Fertilizing
Consistent care is the backbone of a thriving garden. Weekly weeding, monitoring soil moisture, and applying organic fertilizers as needed keep plants healthy and productive. Pruning and removing dead or diseased foliage also help prevent the spread of pests and diseases.
Pest Management Strategies for Small Gardens
Dealing with pests is inevitable, but a proactive approach can minimize damage and maintain a healthy garden. I’ve found that relying on natural solutions, such as neem oil and diatomaceous earth, is effective and environmentally friendly.
Encouraging beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps has been a game-changer, as they naturally keep pest populations in check.
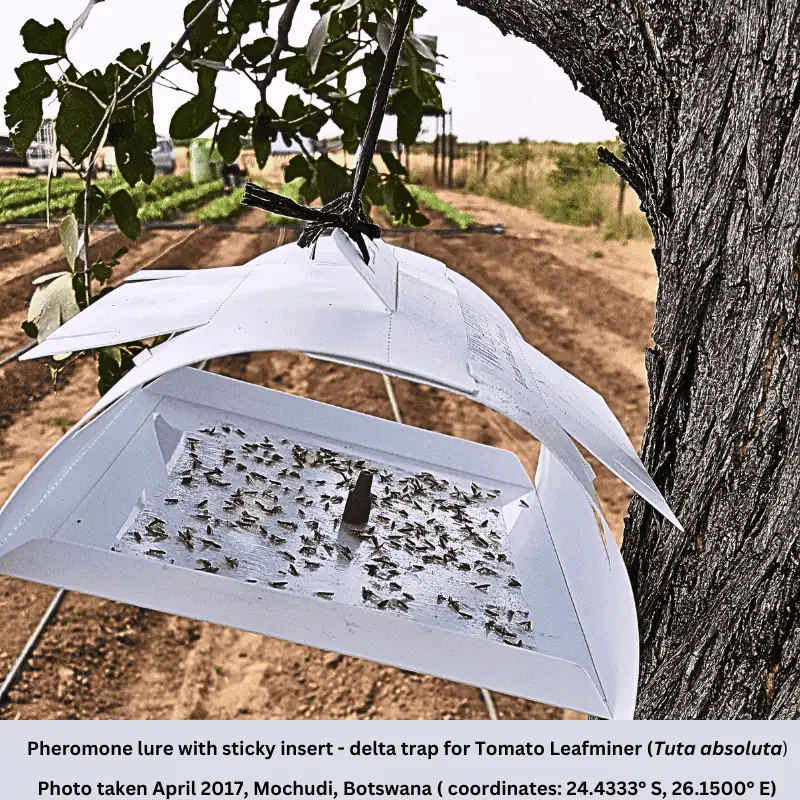
Additionally, pheromone traps and lures can be incredibly effective for monitoring and managing specific pest populations. These traps use chemical signals to attract pests, allowing you to catch them before they cause significant damage.
For example, pheromone traps help control moth species like the Tomato Leaf Miner. I’ve seen these tools reduce pest numbers significantly in larger farming contexts, and they can be scaled down effectively for small garden use.
Pairing this approach with crop rotation and practicing good garden hygiene—such as removing plant debris and regularly inspecting for early signs of infestation—can significantly reduce the risk of pest outbreaks.
Combining these strategies creates a balanced ecosystem that supports your plants and the beneficial organisms that help them thrive.

Create a Monthly Planting Guide for Your Garden
A year-round gardening calendar is essential for staying organized and ensuring that no season is wasted. If you are planting in Northern hemisphere ensuring that you have a plan and stick to it will go a long way – from the planting of peas in March to the harvesting of pumpkins in October, a clear plan allows for the anticipation of seasonal changes and adequate preparation.
For example, focus is placed on early planting and soil improvement in spring, while summer emphasizes pest control and water management.
Include detailed reminders for critical tasks such as soil amendments, planting schedules, and harvesting times and your gardening efforts will be transformed into a more efficient and rewarding practice.
Keeping track of these activities has also enabled learning from past seasons and refining approaches for future success
Seasonal Tasks: What to Do Each Month to Ensure Success
Breaking tasks into monthly goals makes gardening manageable and enjoyable. For example, January is for planning and ordering seeds, while July focuses on pest control and harvesting. Keeping a journal or using a gardening app can help you track your progress and learn from each season.
Gardening is a journey of learning and growth. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your skills, embracing the rhythms of the seasons can transform your small vegetable garden into a productive and fulfilling endeavor.
With patience, creativity, and a bit of trial and error, you’ll be amazed at what you can achieve. Here are 6 useful tips for a temperate maritime climate. Happy planting!







